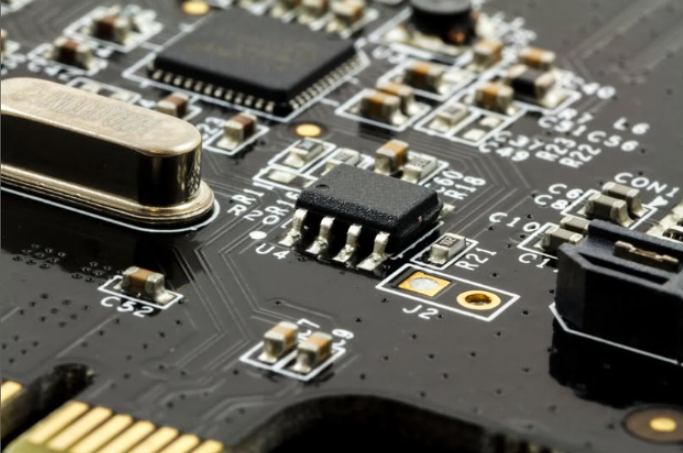
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is a critical process in electronics manufacturing, ensuring that electronic components are correctly placed and soldered onto a PCB. To maintain the highest quality standards and reliability in electronic assemblies, industry professionals adhere to the IPC-A-610 standard. This globally recognized standard sets forth criteria for the acceptability of electronic assemblies, ensuring consistency, reliability, and performance in various applications.
Understanding PCBA and Its Importance
PCBA is the process of assembling electronic components onto a bare printed circuit board (PCB) through soldering techniques such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT). The quality of PCBA directly impacts the performance, reliability, and longevity of electronic devices. Poor assembly practices can result in defects such as cold solder joints, solder bridges, and component misalignment, leading to functional failures and increased costs due to rework or warranty claims.
What is IPC-A-610?
IPC-A-610, also known as “Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies,” is the most widely used inspection standard in the electronics industry. Developed by IPC, the Association Connecting Electronics Industries, IPC-A-610 establishes visual quality requirements for soldered electrical and electronic assemblies. It serves as a guide for manufacturers, quality inspectors, and engineers to ensure compliance with industry best practices.
The standard is frequently updated to incorporate advancements in technology and manufacturing practices. It classifies assemblies into three categories based on their intended use and reliability requirements:
- Class 1: General electronic products where reliability is not a primary concern (e.g., consumer electronics).
- Class 2: Dedicated service electronic products requiring higher reliability and performance (e.g., industrial equipment, telecommunications devices).
- Class 3: High-performance electronic products that demand extreme reliability, such as aerospace, medical, and military applications.
Key Aspects of IPC-A-610 Compliance in PCBA
1. Component Placement and Orientation
Proper component placement ensures optimal circuit functionality and prevents defects like reversed polarity or misalignment. IPC-A-610 provides guidelines for spacing, lead protrusion, and positional accuracy to ensure proper functionality and ease of inspection.
2. Soldering Quality
The standard defines acceptable soldering criteria, including:
- Minimum and maximum solder fillet sizes
- Acceptable solder wetting and coverage
- Prevention of defects such as cold solder joints, solder voids, and bridging
3. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Requirements
SMT is widely used in modern PCBA due to its high efficiency and miniaturization capabilities. IPC-A-610 specifies:
- Proper alignment of SMT components
- Acceptable lead and pad contact
- Criteria for lifted leads, tombstoning, and solder balling defects
4. Through-Hole Technology (THT) Requirements
For through-hole soldering, the standard defines:
- Minimum hole fill percentage
- Lead protrusion requirements
- Acceptable solder joint formation
5. Cleaning and Contamination Control
Contaminants such as flux residues, dust, and moisture can affect PCB performance. IPC-A-610 outlines cleaning requirements to prevent electrical failures caused by conductive debris or corrosion.
6. PCB Damage and Defect Identification
Inspecting for defects such as lifted pads, cracked solder joints, and delamination ensures that defective boards are identified and either reworked or discarded before reaching the customer.
7. Inspection and Testing
Adhering to IPC-A-610 ensures that manufacturers implement proper inspection and testing procedures, such as:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- X-ray Inspection (for BGA and hidden solder joints)
- Functional Testing to verify performance
Benefits of Implementing IPC-A-610 Standards
1. Enhanced Product Reliability
Following IPC-A-610 ensures that PCBA meets stringent quality requirements, reducing the risk of failures in critical applications.
2. Consistency in Manufacturing
Standardized assembly practices minimize variability, ensuring consistent quality across production batches.
3. Reduced Rework and Scrap Costs
By adhering to established acceptability criteria, manufacturers can detect and address defects early, reducing rework costs and material waste.
4. Compliance with Industry Regulations
Many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical, require IPC-A-610 compliance to meet regulatory and safety standards.
5. Customer Satisfaction
High-quality assemblies lead to fewer field failures, enhancing customer confidence and brand reputation.
Conclusion
The IPC-A-610 standard is an essential guideline for ensuring high-quality PCB assemblies. By following its detailed criteria, manufacturers can improve product reliability, reduce defects, and maintain consistency in PCBA production. Whether producing consumer electronics or mission-critical aerospace components, adherence to IPC-A-610 ensures that electronic assemblies meet industry standards and customer expectations. Implementing these best practices ultimately leads to enhanced performance, longevity, and market competitiveness in the electronics industry.